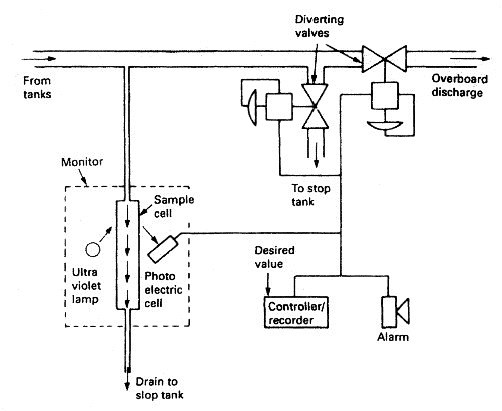
Oil in Water Monitoring System for Merchant Ships
Current regulations with respect to the discharge of oily water from ships set limits
of concentration 15 parts per million. A monitor is
required in order to measure these values and provide both continuous
records and an alarm where the permitted level is exceeded.
The principle used is that of ultra-violet fluorescence. This is the emission of light by a molecule that has absorbed light. During the short interval between absorption and emission, energy is lost and light of a longer wavelength is emitted. Oil fluoresces more readily than water and this provides the means for its detection.
The principle used is that of ultra-violet fluorescence. This is the emission of light by a molecule that has absorbed light. During the short interval between absorption and emission, energy is lost and light of a longer wavelength is emitted. Oil fluoresces more readily than water and this provides the means for its detection.