Home || Diesel Engines
||Boilers||Feed Systems
||Steam Turbines ||Fuel Treatment ||Pumps ||Refrigeration ||
Ships Propeller Shaft -Thrust block & Shaft bearings
The transmission system on a ship transmits power from the engine to
the propeller. It is made up of shafts, bearings, and Finally the propeller
itself. The thrust from the propeller is transferred to the ship through
the transmission system.
The different items in the system include the thrust shaft, one or more
intermediate shafts and the tailshaft. These shafts are supported by the
thrust block, intermediate bearings and the sterntube bearing. A sealing
arrangement is provided at either end of the tailshaft with the propeller
and cone completing the arrangement. These parts, their location and
purpose are shown in Figure below.
Thrust block
The thrust block transfers the thrust from the propeller to the hull of
the ship. It must therefore be solidly constructed and mounted onto a
rigid seating or framework to perform its task.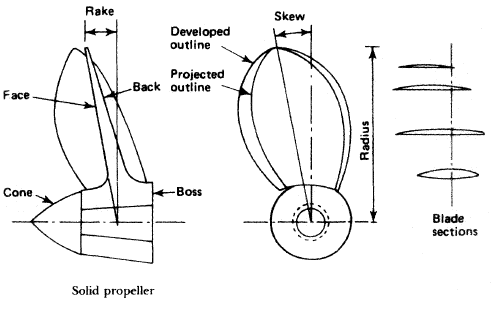
Fig: A solid fixed-pitch propeller

Fig: Thrust block arrangement
The casing of the independent thrust block is in two halves which are
joined by fitted bolts (Figure above). The thrust loading is carried by
bearing pads which are arranged to pivot or tilt. The pads are mounted
in holders or carriers and faced with white metal. In the arrangement
shown the thrust pads extend threequarters of the distance around the
collar and transmit all thrust to the lower half of the casing. Other
designs employ a complete ring of pads.
An oil scraper deflects the oil
lifted by the thrust collar and directs it onto the pad stops. From here it
cascades over the thrust pads and bearings. The thrust shaft is
manufactured with integral flanges for bolting to the engine or gearbox
shaft and the intermediate shafting, and a thrust collar for absorbing the
thrust.

Fig: Propeller shaft arrangement
Shaft bearings
Shaft bearings are of two types, the aftermost tunnel bearing and all
others. The aftermost tunnel bearing has a top and bottom bearing shell
because it must counteract the propeller mass and take a vertical upward
thrust at the forward end of the tailshaft. The other shaft bearings only
support the shaft weight and thus have only lower half bearing shells.
An intermediate tunnel bearing is shown in Figure below.

Fig: Tunnel bearing arrangement
The usual
journal bush is here replaced by pivoting pads. The tilting pad is better
able to carry high overloads and retain a thick oil lubrication film.
Lubrication is from a bath in the lower half of the casing, and an oil
thrower ring dips into the oil and carries it round the shaft as it rotates.
Cooling of the bearing is by water circulating through a tube cooler in
the bottom of the casing.
Related information
- Oil lubricated sterntube bearing, sterntube seals & shafting arrangement
The sterntube bearing serves two important purposes. It supports the tailshaft and a considerable proportion of the propeller weight. It also acts as a gland to prevent the entry of sea water to the machinery space.....
-
Function of solid fixed pitch propeller & Propeller mounting
The propeller consists of a boss with several blades of helicoidal form attached to it. When rotated it 'screws' or thrusts its way through the water by giving momentum to the column of water passing through it. The thrust is transmitted along the shafting to the thrust block and finally to the ship's structure....
- Controllable pitch propeller
A controllable pitch propeller is made up of a boss with separate blades mounted into it. An internal mechanism enables the blades to be moved simultaneously through an arc to change the pitch angle and therefore the pitch....
-
Ships propeller shaft -Thrust block & Shaft bearings
The transmission system on a ship transmits power from the engine to the propeller. It is made up of shafts, bearings, and Finally the propeller itself. The thrust from the propeller is transferred to the ship through the transmission system....
-
Ships steering gear arrangement and testing requirement
The main steering gear is to be capable of putting the rudder over
from 35° on one side to 35° on the other side with the ship at its deepest
draft and running ahead at maximum service speed, and under the same
conditions from 35° on either side to 30° on the other side in not more than
28 seconds.....
-
Ships steering gear electrical control
The electrical remote control system is commonly used in modern installations since it uses a small control unit as transmitter on the bridge
and is simple and reliable in operation.Movement of the bridge transmitter
results in electrical imbalance and current flow to the motor.
.....
-
Ships steering gear telemotor control
Telemotor control is a hydraulic control system employing a transmitter, a receiver, pipes and a charging unit. The transmitter, which is built into
the steering wheel console, is located on the bridge and the receiver is
mounted on the steering gear..
.....
Marine machineries - Useful tags
Marine diesel engines ||Steam generating plant ||Air conditioning system ||Compressed air ||Marine batteries ||Cargo refrigeration ||Centrifugal pump ||Various coolers ||Emergency power supply ||Exhaust gas heat exchangers ||Feed system ||Feed extraction pump ||
Flow measurement || Four stroke engines || Fuel injector || Fuel oil system || Fuel oil treatment ||Gearboxes || Governor ||
Marine incinerator ||
Lub oil filters ||
MAN B&W engine ||
Marine condensers ||
Oily water separator ||
Overspeed protection devices ||
Piston & piston rings ||
Crankshaft deflection ||
Marine pumps ||
Various refrigerants ||
Sewage treatment plant ||
Propellers ||
Power Plants
||
Starting air system ||
Steam turbines ||
Steering gear ||
Sulzer engine ||
Turbine gearing ||
Turbochargers ||
Two stroke engines ||
UMS operations ||
Drydocking & major repairs ||
Critical machinery ||
Deck machineries & cargo gears
|| Control and instrumentation
||Fire protection
||Engine room safety ||
Machinery Spaces.com is about working principles, construction and operation of all the machinery
items in a ship intended primarily for engineers working on board and those who working ashore . For any remarks please
Contact us
Copyright © 2010-2016 Machinery Spaces.com All rights reserved.
Terms and conditions of use
Read our privacy policy|| Home page||

