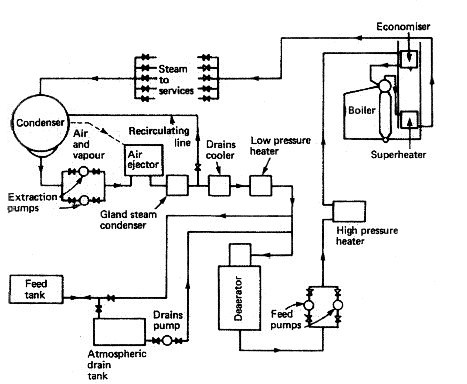
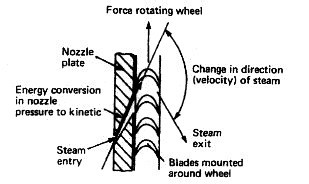
Closed Feed System for Marine Auxiliary Boiler
The feed system completes the cycle between boiler and turbine to
enable the exhausted steam to return to the boiler as feedwater. The
feed system is made up of four basic items: the boiler, the turbine, the
condenser and the feed pump. The boiler produces steam which is
supplied to the turbine and finally exhausted as low-energy steam to the
condenser. The condenser condenses the steam to water (condensate)
which is then pumped into the boiler by the feed pump.