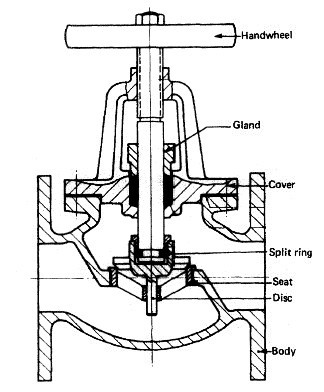
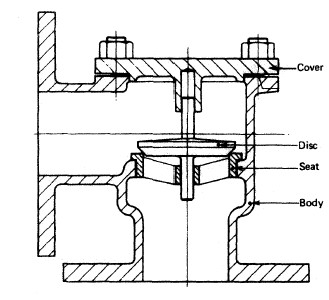
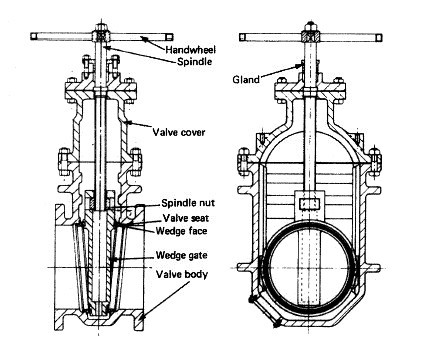
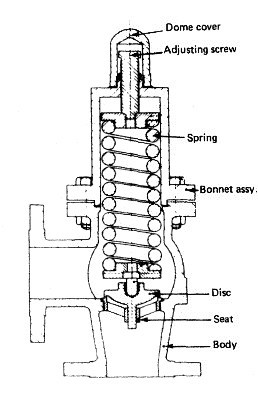
Various valves arrangement for machinery spaces piping system
Valves are provided in a piping system to regulate or stop the liquid
flow. Various types exist in a machinery space with their associated particular function or
advantages.
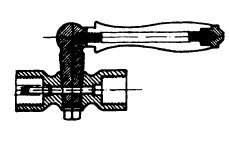
Cock: A cock is used in small-bore pipework and is joined to adjacent pipework by a compression coupling. A cock can restrict or close an internal passage by moving a central plug, usually by an external lever. An example of a straight-through cock is given in Figure
Cock: A cock is used in small-bore pipework and is joined to adjacent pipework by a compression coupling. A cock can restrict or close an internal passage by moving a central plug, usually by an external lever. An example of a straight-through cock is given in Figure