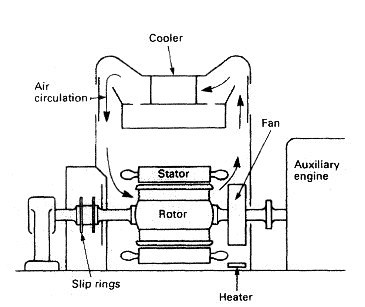
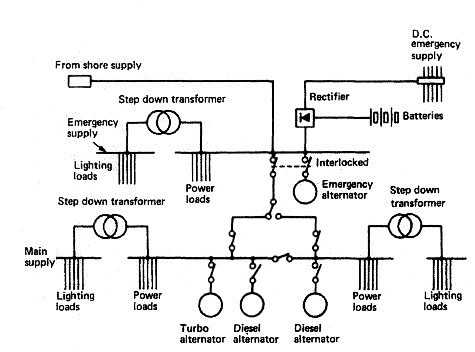
Electrical Plant and Distribution System for Ships A.C. Generators
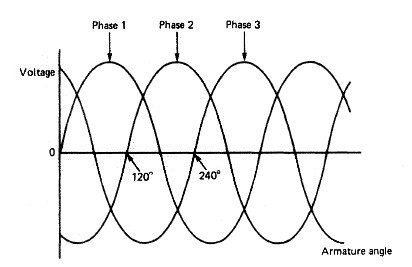
Alternating current is a form of electricity in which the current
alternates in direction (and the voltage alternates in polarity) at a frequency defined by
the generator (usually between 50 and 60 times per second, i.e., 50 – 60 hertz). AC was
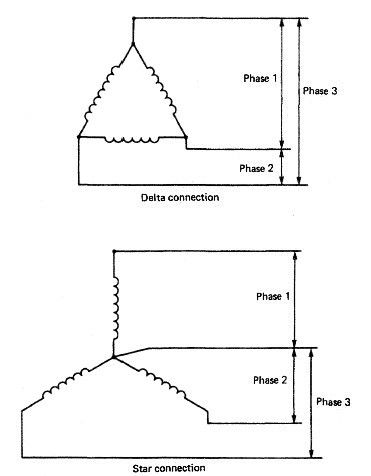
adopted for power transmission in the early days of electricity supply because it had
two major advantages over direct current (DC): its voltage could be stepped up or down
according to need using transformers, and it could be interrupted more easily than DC.
Neither advantage is as relevant today as it once was because power electronics can
solve both issues for DC.