
Steam to steam generator working principle and operational procedure
Steam-to-steam generators produce low-pressure saturated steam for domestic and other services. They are used in conjunction with watertube boilers to provide a secondary steam circuit which avoids any possible contamination of the primary-circuit feedwater. The arrangement may be horizontal or vertical with coils within the shell which heat the feedwater.

- Flow Measurement
- Four Stroke Engines
- Two Stroke Engines
- Fuel Injection System
- Fuel Oil System
- Lub Oil filters
- MAN B&W Engine
- Sulzer Diesel Engine
- Marine Condensers
- Oily Water Separator
- Overspeed Protection
- Piston & Piston rings
- Crankshaft Deflection
- SewageTreatment Plant
- Starting Air System
- Emergency Power Supply
- UMS Operations
- Drydocking & Repairs
- Critical Machinery
- Deck Machineries
- Control Instrumentation
- Engine Room Safety
- Home
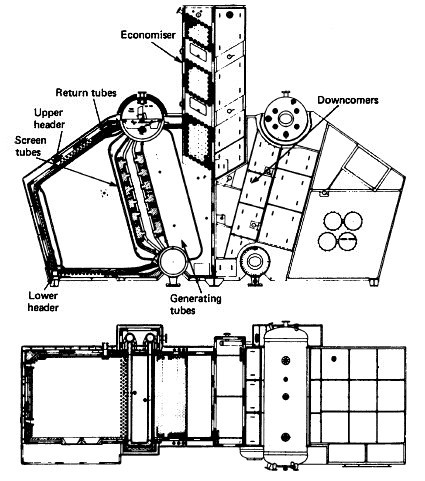
Fig:Water tube boiler
Raising Steam
Fuel Quality
Boilers are usually fired using heavy fuel oil. If it is necessary because of insufficient steam for fuel heating, to use Diesel Oil or other lower viscosity fuel a single pressure jet burner with the smallest available tip is to be used. If this is not available, then the smallest steam atomising or steam assisted tip can be used, provided that the steam connections are blanked off. The boiler is to revert to firing on heavy fuel oil once appropriate steam heating pressure is reached.
Purging
Should the burner fail to ignite, or flame failure occur, then it is essential that the furnace is visually examined for unburned fuel and purged before any attempt is made to re-ignite the burner. If the boiler furnace or furnaces are fitted with automatic purging systems then these must be fully operational. If the furnace or furnaces are not fitted with automatic purging sequence systems or they are not operational then prior to burner ignition, and on each subsequent occasion prior to re-igniting the burner or burners the furnace spaces are to be purged using the forced draft fans to give a minimum of five full changes of furnace air.
Manual Firing
If manual firing has to be resorted to, then the procedure must be in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions and as agreed with the Technical Department of the relevant management office.
Firing
The procedure for firing must be in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions. Heating should be gradual and uniform, starting with one burner using the smallest tip available. A period of six hours should normally be allowed for raising steam, but in cases where repairs to refractory, or parts subject to pressure, have been carried out the period should be extended to 24 hours with alternate registers used.
Flow through Superheaters
Steam flow through superheaters must be maintained at all times. In cases of emergency when steam is required at short notice the boiler manufacturer’s instructions are to be adhered to.
Venting
Throughout the steam raising process, provision is to be made for venting all air from the boiler. This should be done solely by means of a designated air release cock or, if this is not fitted, by means of the steam pressure gauge cock. Under no circumstances are the steam connections of the water level gauge glasses to be used for venting purposes.
Related Info:
Requirement for various boiler types on board cargo ships
Safety precautions for working with marine boiler
General arrangement for marine boiler
Water tube boilers
Fire tube boilers
The use of boiler mountings
Combustion process - supply of air
Various designs burners
Purity of boiler feedwater
Boiler feedwater treatment
The steam to steam generator
Combustion process - supply of fuel oil
Safety valves
Water level gauges
Double evaporation boilers
Exhaust gas heat exchangers
Safety precautions
Marine machineries - Useful tags
Marine diesel engines ||Steam generating plant ||Air conditioning system ||Compressed air ||Marine batteries ||Cargo refrigeration ||Centrifugal pump ||Various coolers ||Emergency power supply ||Exhaust gas heat exchangers ||Feed system ||Feed extraction pump || Flow measurement || Four stroke engines || Fuel injector || Fuel oil system || Fuel oil treatment ||Gearboxes || Governor || Marine incinerator || Lub oil filters || MAN B&W engine || Marine condensers || Oily water separator || Overspeed protection devices || Piston & piston rings || Crankshaft deflection || Marine pumps || Various refrigerants || Sewage treatment plant || Propellers || Power Plants || Starting air system || Steam turbines || Steering gear || Sulzer engine || Turbine gearing || Turbochargers || Two stroke engines || UMS operations || Drydocking & major repairs || Critical machinery || Deck machineries & cargo gears || Control and instrumentation ||Fire protection ||Engine room safety ||
Machinery Spaces.com is about working principles, construction and operation of all the machinery items in a ship intended primarily for engineers working on board and those who working ashore . For any remarks please Contact us
Copyright © 2010-2016 Machinery Spaces.com All rights reserved.
Terms and conditions of use
Read our privacy policy|| Home page||
Fuel Quality
Boilers are usually fired using heavy fuel oil. If it is necessary because of insufficient steam for fuel heating, to use Diesel Oil or other lower viscosity fuel a single pressure jet burner with the smallest available tip is to be used. If this is not available, then the smallest steam atomising or steam assisted tip can be used, provided that the steam connections are blanked off. The boiler is to revert to firing on heavy fuel oil once appropriate steam heating pressure is reached.
Purging
Should the burner fail to ignite, or flame failure occur, then it is essential that the furnace is visually examined for unburned fuel and purged before any attempt is made to re-ignite the burner. If the boiler furnace or furnaces are fitted with automatic purging systems then these must be fully operational. If the furnace or furnaces are not fitted with automatic purging sequence systems or they are not operational then prior to burner ignition, and on each subsequent occasion prior to re-igniting the burner or burners the furnace spaces are to be purged using the forced draft fans to give a minimum of five full changes of furnace air.
Manual Firing
If manual firing has to be resorted to, then the procedure must be in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions and as agreed with the Technical Department of the relevant management office.
Firing
The procedure for firing must be in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions. Heating should be gradual and uniform, starting with one burner using the smallest tip available. A period of six hours should normally be allowed for raising steam, but in cases where repairs to refractory, or parts subject to pressure, have been carried out the period should be extended to 24 hours with alternate registers used.
Flow through Superheaters
Steam flow through superheaters must be maintained at all times. In cases of emergency when steam is required at short notice the boiler manufacturer’s instructions are to be adhered to.
Venting
Throughout the steam raising process, provision is to be made for venting all air from the boiler. This should be done solely by means of a designated air release cock or, if this is not fitted, by means of the steam pressure gauge cock. Under no circumstances are the steam connections of the water level gauge glasses to be used for venting purposes.
Related Info:
- Marine steam turbines operating procedure
- Impulse steam turbine and reaction steam turbine
- Turbine control and protection
- Various turbine gearing -Epicyclic gearing,Helical gearing,Flexible coupling &Turning gear
- Construction of the steam to steam generator - how it works
- Cross compound steam turbine arrangement for marine use
The steam turbine has until recently been the first choice for very large power marine propulsion units. Its advantages of little or no vibration, low weight, minimal space requirements and low maintenance costs are considerable. Furthermore a turbine can be provided for any power rating likely to be required for marine propulsion.
More.....
The steam turbine is a device for obtaining mechanical work from the energy stored in steam. There are two main types of turbine, the 'impulse' and the 'reaction'. The names refer to the type of force which acts on the blades to turn the turbine wheel.
More.....
A turbine protection system is provided with all installations to prevent damage resulting from an internal turbine fault or the malfunction of some associated equipment. Arrangements are made in the system to shut the turbine down using an emergency stop and solenoid valve.
More.....
Helical gears have been used for many years and remain a part of most systems of gearing. Epicyclic gears with their compact, lightweight, construction are being increasingly used in marine transmissions.
More.....
Steam-to-steam generators produce low-pressure saturated steam for domestic and other services. They are used in conjunction with watertube boilers to provide a secondary steam circuit which avoids any possible contamination of the primary-circuit feedwater. .
More.....
Compounding is the splitting up, into two or more stages, of the steam pressure or velocity change through a turbine. Pressure compounding of an impulse turbine is the use of a number of stages of nozzle and blade to reduce progressively the steam pressure..
More.....
Requirement for various boiler types on board cargo ships
Safety precautions for working with marine boiler
General arrangement for marine boiler
Water tube boilers
Fire tube boilers
The use of boiler mountings
Combustion process - supply of air
Various designs burners
Purity of boiler feedwater
Boiler feedwater treatment
The steam to steam generator
Combustion process - supply of fuel oil
Safety valves
Water level gauges
Double evaporation boilers
Exhaust gas heat exchangers
Safety precautions
Marine machineries - Useful tags
Marine diesel engines ||Steam generating plant ||Air conditioning system ||Compressed air ||Marine batteries ||Cargo refrigeration ||Centrifugal pump ||Various coolers ||Emergency power supply ||Exhaust gas heat exchangers ||Feed system ||Feed extraction pump || Flow measurement || Four stroke engines || Fuel injector || Fuel oil system || Fuel oil treatment ||Gearboxes || Governor || Marine incinerator || Lub oil filters || MAN B&W engine || Marine condensers || Oily water separator || Overspeed protection devices || Piston & piston rings || Crankshaft deflection || Marine pumps || Various refrigerants || Sewage treatment plant || Propellers || Power Plants || Starting air system || Steam turbines || Steering gear || Sulzer engine || Turbine gearing || Turbochargers || Two stroke engines || UMS operations || Drydocking & major repairs || Critical machinery || Deck machineries & cargo gears || Control and instrumentation ||Fire protection ||Engine room safety ||
Machinery Spaces.com is about working principles, construction and operation of all the machinery items in a ship intended primarily for engineers working on board and those who working ashore . For any remarks please Contact us
Copyright © 2010-2016 Machinery Spaces.com All rights reserved.
Terms and conditions of use
Read our privacy policy|| Home page||
