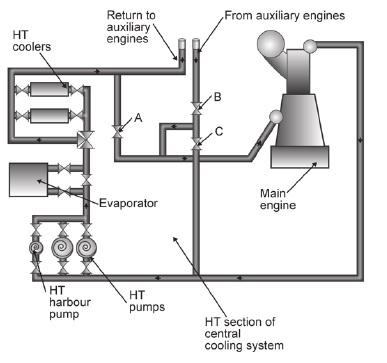
Fresh water & Sea water Cooling System Maintenance
The heat produced by running machinery, must be removed to ensure the
satisfactory functioning of the equipment. Cooling is achieved primarily
through circulation of water, oil and air but the abundant supply of sea water is
normally reserved for use as an indirect coolant because the dissolved salts
have a great potential for depositing scale and assisting in the setting up of
galvanic corrosion cells. Pollution of coastal areas by industrial and other
wastes has added to the problems of using sea water as a coolant.