How to avoid scavenge fires - Internal combustion engine procedure
A basic part of the cycle of an internal combustion engine is the supply
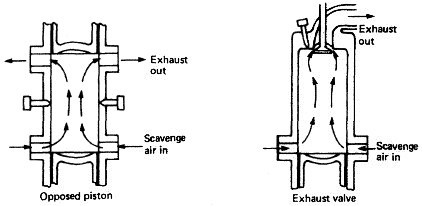
of fresh air and removal of exhaust gases. This is the gas exchange
process. Scavenging is the removal of exhaust gases by blowing in fresh
air. Charging is the filling of the engine cylinder with a supply or charge
of fresh air ready for compression. With supercharging a large mass of air
is supplied to the cylinder by blowing it in under pressure.
Efficient scavenging is essential to ensure a sufficient supply of fresh air for combustion. Cylinder oil can collect in the scavenge space of an engine. Unburned fuel and carbon may also be blown into the scavenge space as a result of defective piston rings, faulty timing, a defective injector, etc.
Efficient scavenging is essential to ensure a sufficient supply of fresh air for combustion. Cylinder oil can collect in the scavenge space of an engine. Unburned fuel and carbon may also be blown into the scavenge space as a result of defective piston rings, faulty timing, a defective injector, etc.